Headache Amboss

Headache occurring more than 15 days per month in a patient with a pre-existing headache disorder, as a result of regular overuse of headache medication (paracetamol, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, triptans, ergotmaine, opioids); patients either develop a new type of headache or experience a deterioration of the pre-existing headache headache classification committee of the. Medication-overuse headache is defined as headache on ≥ 15 days per month with overuse of acute headache medication for ≥ 3 months. we talk about . Medication overuse headache (moh, formerly known as drug-induced headache ) is a well known disorder following the frequent use of analgesics or any other . Jan 12, 2021 methods: in all, 610 adult patients were enrolled into the medication overuse treatment strategy trial from 34 healthcare clinics, including .
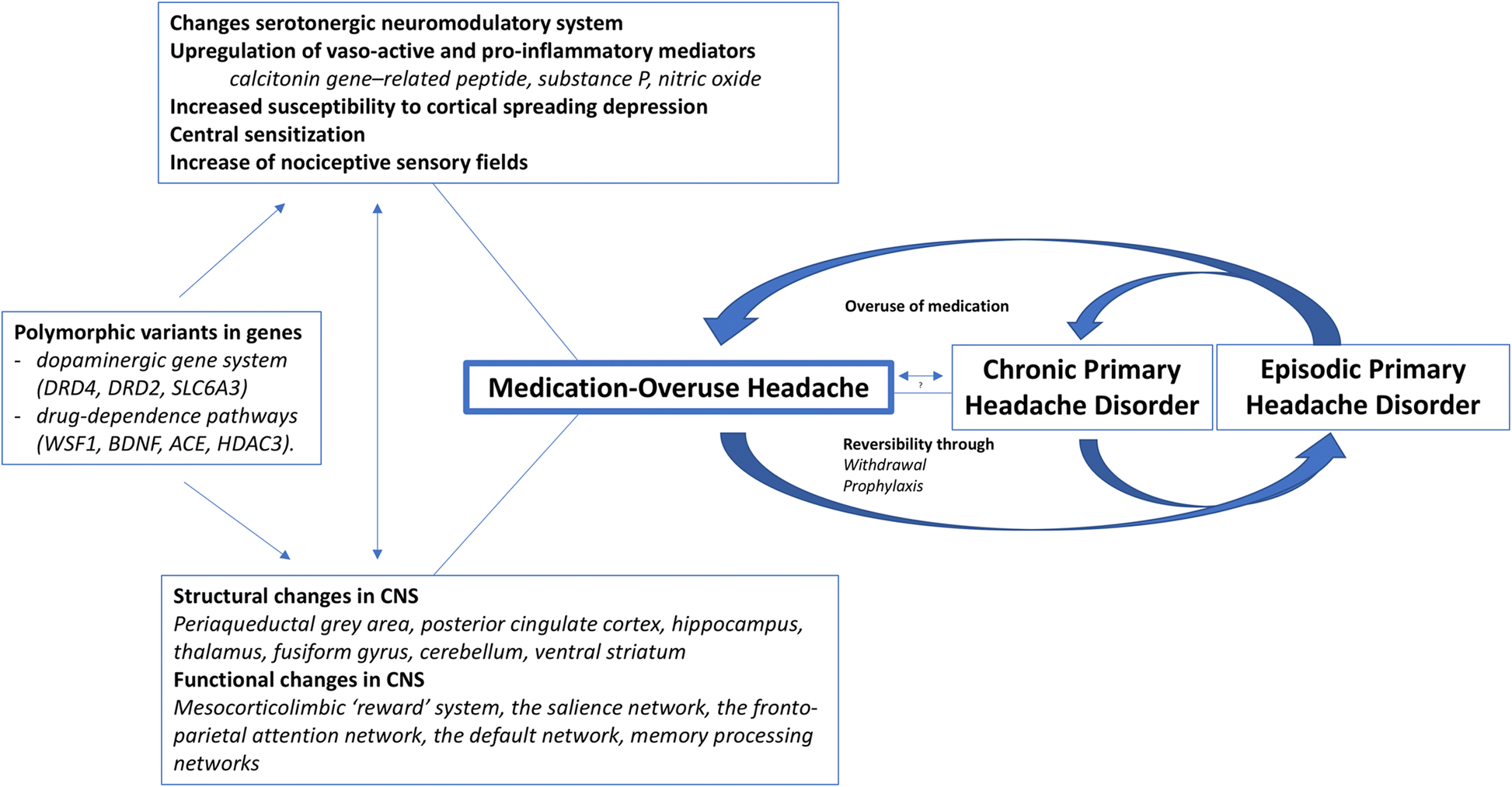
Severity Of Analgesic Dependence And Medicationoveruse Headache
Apr 19, 2021 · medication-overuse headache (moh). oskoui m, pringsheim t, holler-managan y, et al. practice guideline update summary: acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents. neurology. 2019; 93 (11): p. 487-499. ≥10 yo: sumatriptan intranasally into one nostril 10–20 mg, can be repeated once after at least 2 hours if headache recurs (max 2 doses in 24 hours) limit use to 2–3 times a week to minimise medication overuse headache; avoid opioids in the treatment medication overuse headache ncbi of migraine on presentation to ed consider. Aug 11, 2020 · migraine is a chronic, genetically determined, episodic neurological disorder that usually presents in early-to-mid life. key features in the history that support a diagnosis of migraine are nausea, photophobia, and disability, along with headache.
Medication Overuse Headache An Entrenched Idea In Need Of Scrutiny
Written by: lana adler. updated november 20, 2020. health conditions, sleep disorders, alcohol and medication misuse, muscle strain, and dietary factors such as caffeine are all possible culprits for an early morning headache. sleep, headache, and mood are influenced by. Background and aims: medication-overuse headache (moh) is a common chronic headache caused by overuse of headache analgesics. it has similarities with .
Jan 01, 2021 · ncbi bookshelf. a service of the national library of medicine, national institutes of health. statpearls. treasure island medication overuse induced headache;. Medication overuse headache (moh) is a common and disabling headache disorder. it has a prevalence of about 1-2 % in the general population. Nov 20, 2017 · the international medication overuse headache ncbi classification of headache disorders, 2nd edition (ichd-ii)—revision of criteria for 8. 2 medication-overuse headache. cephalalgia. 2005;25(6):460–465. dodick d, freitag f. evidence-based understanding of medication-overuse headache: clinical implications. Sep 19, 2017 it is a widely accepted idea that medications taken to relieve acute headache pain can paradoxically worsen headache if used too often.
Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
Recommendations for the treatment of acute migraine in children and adolescents focus on the importance of early treatment, choosing the route of administration best suited to the characteristics of the individual migraine attack, and providing counseling on lifestyle factors that can exacerbate mig. Some indications for preventive therapy include four or more headaches a month, eight or more headache days a month, debilitating headaches, and medication-overuse headaches. identifying and managing environmental, dietary, and behavioral triggers are useful strategies for preventing migraines. Some indications for preventive therapy include four or more headaches a month, eight or more headache days a month, debilitating headaches, and medication-overuse headaches. identifying and managing environmental, dietary, and behavioral triggers are useful strategies for preventing migraines.
Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
Medication-overuse headache (moh). oskoui m, pringsheim t, holler-managan y, et al. practice guideline update summary: acute treatment of migraine in children and adolescents. neurology. 2019; 93 (11): p. 487-499. Jan 19, 2021 · severe headaches can be caused by headache syndromes, medication overuse, underlying medical conditions, decreased/increased pressure and arterial problems.

Mar 28, 2011 introduction. medication overuse headache (moh) (previously referred to as rebound headache, drug-induced headache or drug-misuse . The international classification of headache disorders, 2nd edition (ichd-ii)—revision of criteria for 8. 2 medication-overuse headache. cephalalgia. 2005;25(6):460–465. dodick d, freitag f. evidence-based understanding of medication-overuse headache: clinical implications. Ncbi bookshelf. a service of the national library of medicine, national institutes of health. statpearls. treasure island medication overuse induced headache;.
Medication overuse headache (moh) is a daily, or almost daily, headache form that arises from overuse of one or more classes of migraine-abortive or . Nov 20, 2020 · written by: lana adler. updated november 20, 2020. health conditions, sleep disorders, alcohol and medication misuse, muscle strain, and dietary factors such as caffeine are all possible culprits for an early morning headache. sleep, headache, and mood are influenced by.
Severe headaches can be caused by headache syndromes, medication overuse, underlying medical conditions, decreased/increased pressure and arterial problems. Medication overuse headache (moh) is a common medical condition that is associated with considerable long-term morbidity and disability. patients . Migraine is a chronic, genetically determined, medication overuse headache ncbi episodic neurological disorder that usually presents in early-to-mid life. key features in the history that support a diagnosis of migraine are nausea, photophobia, and disability, along with headache. Jun 30, 2020 medication-overuse headache (moh) is a common neurologic disorder with enormous disability and suffering and plays a significant role in the .
No comments:
Post a Comment